




The present research aimed at developing and evaluating a vesicular drug carrier system for topical delivery of Repaglinide to provide sustained drug delivery. Repaglinide ethosomes were formulated using the method of thin film hydration by soya lecithin and evaluated for percent entrapment efficiency, vesicle size, percent drug content, surface morphology, and in-vitro drug release. The ethosomes were prepared by varying the variables such as concentrations of soya lecithin and ethanol, while entrapment efficiency and drug release were the chosen responses. Ethosomal formulation was optimized using the 32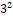 factorial design. The vesicle size of optimized batch was found to be 198.92 nm with zeta potential of -13.42 mV. The % entrapment efficiency was found to be 92.40 % and percent drug release of ethosomal gel was found to be 73.24%. Optical microscopic and scanning electron microscopic observations showed formation of spherically shaped vesicles. The in-vitro drug release of the formulation increases with increase in ethanol concentration and decrease in lipid concentration.
factorial design. The vesicle size of optimized batch was found to be 198.92 nm with zeta potential of -13.42 mV. The % entrapment efficiency was found to be 92.40 % and percent drug release of ethosomal gel was found to be 73.24%. Optical microscopic and scanning electron microscopic observations showed formation of spherically shaped vesicles. The in-vitro drug release of the formulation increases with increase in ethanol concentration and decrease in lipid concentration.